Do-it-yourself heat pump
The variety of heating systems on the market gives a person an “alluring illusion” of freedom of choice. But think about it … In reality, we are bound hand and foot. The gas line can be located quite far (oh, money, some money), add to this the hassle associated with a lengthy voyage to various authorities; Yes, that there is hassle, this is a lot of lost time and all the same crispy bills. We go further: liquefied gas is a good option, but, of course, not cheap either. A diesel engine means decent operating costs and a number of significant inconveniences: the need to deliver fuel, the fragrance is “something else” plus such a boiler needs regular maintenance. What about electricity? Of course, safe, convenient, environmentally friendly … but also the most expensive. A solid alternative to popular (traditional) heating schemes can be the use of heat pump units, drawing energy from nature. Heat pump do it yourself – a real opportunity to reduce heating costs.
Content
- Heat pump: haven’t you heard?
- Quick payback on installation
- Heat pump – principle of operation
- Did you know?
- Convincing experience
- Feasibility of using free resources
- Do-it-yourself heat pumps – why not?
- Energy Sources for Heat Pumps: Features
- Energy Provider – Well
- The energy resource of the reservoir
- Earth heat use
- Air circuit – money from the air
- Calculation of the heat pump making useful homemade
Heat pump: haven’t you heard?
The energy source for the heat pump is electricity. Stop stop. Do not be alarmed. The pump does not produce heat, it only collects it: to get a kilowatt of thermal energy, it will have to “spend” only about 200 watts. Surprised? That’s the same.
Quick payback on installation
The heat pump is ideal for new construction: in this case, you can take into account all the nuances characteristic of the heating system, and the unit itself will be able to fully reveal all its “capabilities”. But even in an existing system it is quite easy to implement. Is it cost effective? The question is relevant and “legal.” Well, for the sake of objectivity, it is worth noting that the “integration” of a heat pump from A to Z will cost much more than similar manipulations with gas or diesel equipment. But! A significant plus is that operating costs make it possible to seriously talk about its payback in a couple of years.
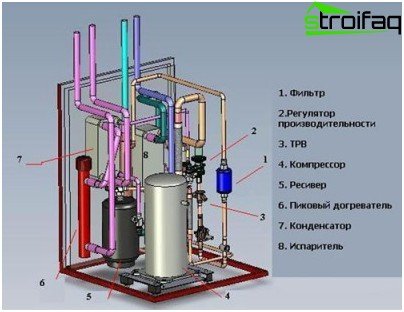
Heat pump circuit
Low energy consumption, high level of comfort, unpretentiousness in service, presentable “appearance”, safety allow us to talk about heat pumps as one of the most promising installations for heating.
Heat pump – principle of operation
When discussing the principle of operation of a heat pump, most often, however strange it may seem at first glance, they recall the refrigerator. Why? It’s just that the operation of the VT is based on the technical principle of the refrigerator. The refrigerator removes heat from its “insides” and transfers it “out” through the grill on the back wall. The heat pump, on the contrary, absorbs energy from the environment and “delivers” it to the heating system.
The source of heat can be air, earth, water – the “classic” natural elements. The advantage of air is its availability in any situation. But the Earth’s bowels with water are not without their “pluses” – after all, they are the optimal heat accumulators against the background of a relatively constant (throughout the year) temperature.
Did you know?
For some, this will become a sensation, for some, it’s not, but the heat pump can not only “warm” the building, but also cool it. Cooling can be carried out according to two technologies: passive and active. The first method (natural) is based on the fact that in “amphibian” bowels the summer temperature is lower than in rooms, respectively, buildings can be cooled directly. The second way is real air conditioning. Reversible VT provides the ability to control the flow of refrigerant. All the “heat” from the house is transferred to the refrigerant and is discharged through the heat exchanger.
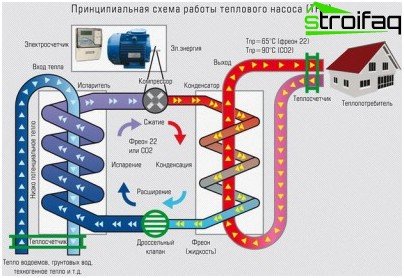
The principle of operation of a heat pump is based on the absorption of heat energy borrowed from air, earth, water
Convincing foreign experience
The heat pump, as a technology of “production” of heat, has become widespread in many “progressive” countries: hundreds of thousands of such plants are installed annually. It is particularly popular and in demand in the countries of the current European Union, China and, naturally, the United States..
The rapid development of this method of providing heat to the final consumer is based not only on the uniqueness of the system as such, but also on powerful state support – the buyer’s costs are partially reimbursed.
… Finally, a truly massive interest in TN came to the “native spaces”. But quite often, information about the units and the technology itself is conveyed by the manufacturer to the target audience somewhat distorted – for the sole purpose of “pushing” a novelty. True, in spite of all the carefully thought-out marketing moves, sales, however, do not grow much. After all, the fact remains that there is no getting away from big starting investments.
Not everyone is ready to selflessly empty their wallet just for the promise of saving money on heat supply.
Given all of the above, it can be assumed that the buyer will be able to look at “exotic” equipment with a high degree of confidence if he knows in what cases it is a really profitable and irreplaceable thing.
Feasibility of using free resources
If gas is supplied to the house, it does not make sense to install a VT – this is unjustified in terms of financial costs.
But in the absence of the ability to supply main gas (as an option, the extremely high cost of this event), the installation of a heat pump will be an excellent solution to heat supply issues.
Equipment on diesel fuel, liquid gas, etc., will not be able to compete with the vehicle neither in terms of safety, nor in terms of comfort, nor in operating costs..
Do-it-yourself heat pumps – why not?
Despite all the “progressiveness” of the heat pump technology, the unit can be mounted with your own hands..

Do-it-yourself heat pump: one of the options for its appearance
Before you start to “create”, objectively assess the condition of the house.
Thermal insulation, if necessary, should be improved – modern building materials to help you. Schematic diagram of the heat pump “includes” several components: compressor, evaporator, condenser and thermostatic valve. Safety devices, such as a receiver, a filter drier and a viewing window, can not be used here – when assembling the system manually, you are unlikely to be able to foresee all the “factory things” and create the unit “as if from a factory”.
- The role of the compressor is best “given” to the most silent equipment: you can take, for example, a compressor from an imported air conditioner. Using the L-300mm brackets, it is attached to the wall;

Mounting the compressor to the brackets
- A special tank (volume – 120 l) made of stainless steel is needed for the condenser. It is cut into 2 parts; a coil is inserted from a copper pipe along which freon will move. Then the tank must be welded back, not forgetting to weld several technical threaded joints;
- As a heat exchanger pipe, you can use a copper refrigeration pipe or a regular plumbing pipe (clean);
- The pipe must be rolled into a coil (wrap around a cylinder). The edges of the turns should be fixed (aluminum rails) to increase the equidistance of the loops. To bring out its ends with the help of plumbing junctions;
- Freonovod coil: the entrance to the capacitor from above – the output from below. Due to this, bubbles will not form;
- The evaporator does not require a high temperature, so the plastic barrel capacity (capacity of about 100 l) is ideal for this purpose;
- The drain and water supply can be “carried out” by ordinary sewer pipes with gaskets;
- Fix the evaporator using the L-400mm brackets;

A suitable plastic container can be used as an evaporator; it must be installed on a stand fixed with brackets
- Thermostatic expansion valve sold separately (consider compatibility with your “work of art”);
The process of soldering, filling with freon, etc., we still recommend trusting the hands of professionals (safety first); and in general, an “experienced look” before putting the unit into operation will not harm anyone. Do not forget about automation issues – you will need a single-phase start relay, fuses, temperature switches.
Attention! The creation of such equipment without certain skills and deep knowledge in the field of physics is a risk. If you doubt your strength and competence, do not improvise! A superficial familiarization with the principle of operation and the design of the heat pump is not enough to design the unit with your own hands!
Energy Sources for Heat Pumps: Features
Energy Provider – Well
When using rocky rock as a heat source, the pipeline sinks into the well.
You can use one deep, you can several shallow (of course, cheaper). After all, the main thing is the total estimated depth. About 50-60 W of heat energy per meter of well.

Well as a heat source
Correspondingly, for the installation of heat pumps with a capacity of 10 kW, a total well depth (or one well depth) of 170-200 m.
The energy resource of the reservoir
If the role of the heat source is played by the nearest body of water, the circuit is laid to the bottom. The pond should be flowing and not resemble a modest puddle. About 30 watts of energy is consumed per meter of pipeline. To install a VT (10 kW), it is necessary to lay a circuit a little more than 300 m long.

Pond as a heat source
So that it does not come up, 5 kg of cargo is installed per linear meter of the pipeline. Positive water temperature even in winter is one of the most significant advantages of this option..
Earth heat use
Choosing a plot of land as the heat source, the pipeline must be “buried” to a depth slightly greater than the depth of freezing (depending on the region) of the soil. There is no need for special soil preparation, the use of various backfills, but preference should still be given to wetter soil (ideally, with the proximity of groundwater).

Earth circuit as a heat source
Although dry soil is by no means prohibited: it is true that it will require an increase in the length of the contour. For our heat pump we need 330-500 m of circuit. For laying thereof, an area of 400-600 m? Is required. The minimum distance between adjacent pipelines is 0.8 m. The correct calculation and laying of the contour will avoid negative impact on garden plantings, you can successfully use your “plantations” further.
Air circuit – money from the air
You can “collect” energy from the surrounding air. If it is not possible to place an earthen collector, then this type of pumping unit is the most optimal option.

Air circuit as a heat source
Heat pump calculation
What data should be considered when calculating a heat pump? An exciting question, which in no case can be ignored.
An approximate list of fundamental factors in the calculation:
- purpose of the building;
- total area of the building;
- number of floors, the area of each of them;
- ceiling height;
- the desired (required) temperature regime in the building;
- walls (material, layers, thickness);
- type and total area of glazing;
- floor (material, layers, thickness);
- roof (material, layers, thickness);
- the presence of a ventilation system, its performance;
- the need for hot water, the number of parsing points;
- heating appliances and their type;
- presence / absence of a land plot / nearby reservoir;
- presence / absence of restrictions on electricity.
Installing a heat pump means gaining real freedom: from now on you are independent of the “fuel economy”, your household safety has moved to a radically new level, and saved financial resources “warm” your pocket.






