Electric heating boilers
The modern construction market offers potential consumers an impressive variety of boilers. Accordingly, the resolution of heating issues in a private country house or ordinary city apartment is no longer a “problem of the century.” “Near by” is this or that type of fuel missing? No problem! You will always be able to find worthy alternatives, one of which may be electric heating boilers.
Content
- Electric boilers in autonomous heating systems
- Classification of electric boilers
- TEN new electric coppers
- Electrode type equipment
- Electric boilers on resistive and induction elements
Electric boilers in autonomous heating systems
Electric heating, undoubtedly, is one of the most environmentally friendly ways to “warm” your home and not pollute the environment with harmful “mining”. Double-circuit electric heating boilers are like a personal mini-boiler, because they not only heat the room, but also “give out” hot water for domestic needs.
An electric boiler can become both the main source of heat in your monastery, and a “partner” for other boilers – gas, diesel, solid fuel. The presence in the system of another backup unit that can run on liquid or cheap solid fuel is one of the ways to save electricity.
How is the heating process carried out in this case??
- the heated premises of the building are initially heated with the help of a backup boiler;
- electric boiler (automatic mode) maintains the required temperature.
This equipment is manufactured in wall and floor versions. The power of the first ranges from 5 to 60 kW. Devices with a power of more than 60 kW can only be floor mounted..
They “feed” from a single-phase or three-phase electric network (220 V and 380 V, respectively). To operate equipment that consumes more than 12 kW, only a three-phase network is used.

Wall-mounted electric boiler: a harmonious addition to the interior, you can install it in any room
The coolant in electric boilers is water or non-freezing liquids – antifreezes (naturally, allowed for heating systems).
Note! The instruction manual for the equipment is an unusually useful thing. Reading it in a timely manner will help you avoid annoying misunderstandings..
Classification of electric boilers
Electric boilers differ among themselves in the way of heating the coolant. Their main types:
- indirect heating: heating element – rheostat cartridge (PETN). It is installed in a heat exchanger tank;
- direct heating – electrode electric water heating boilers. The current, passing through the water and generating heat, heats it;
- induction.
TEN new electric coppers
The principle of operation of this equipment is based on the “conversion” of electricity into heat by means of heating elements (tubular heaters) mounted in a tank (steel) heat exchanger. TEN heats the heat carrier which circulates in a heating system and heats rooms.
Control over the functioning of the apparatus is carried out by the control unit. Heating is controlled by a room temperature controller: it responds to a decrease in temperature by a signal about the need to turn on the heating mode. The necessary working pressure of the heat carrier is achieved by means of a circulation pump. The internal temperature sensor maintains the coolant temperature. Upon reaching the required temperature values in the premises, the heating mode is turned off, and then, after some time, the circulation pump is also turned off, due to which the “coolant” is carried out.
The use of room controllers saves from 20% to 30% of electricity.
The main advantage of this type of boilers is the absence of electrical contact between the fuel element and the coolant, respectively, there is practically no leakage current, which means that along with them you can use emergency automation, for example, RCD (residual current circuit breakers), etc..
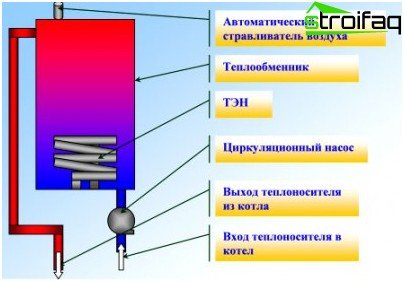
The device and principle of operation of the electric heating boiler
Their power does not depend on the nature of the coolant, its temperature – it varies only within the limits of the voltage fluctuation of the supply network. It is easy to implement stepwise (electronic control system) or smooth regulation (microprocessor control unit).
Of course, these electrical units have their drawbacks: the resource of heating elements is limited, and even premature burnout is not excluded. When buying, be sure to pay attention to the possibility of replacing them..
In addition, the heater is a “great place” for scale, craving to disable the device as soon as possible.
Measures should be taken to reduce water hardness!
TENOV units are electric double-circuit boilers and single-circuit devices. A double-circuit electric boiler is both heating and hot water.
Usually, due to their low weight and modest dimensions, they are wall-mounted, but there are also powerful floor models.
This is the most common type of electric boiler..
Electrode type equipment
Electrode hot water electric boilers are much less common.
Water heating in them occurs due to the release of heat generated during the passage of current “through” the coolant (conductor) directly, without the participation of “intermediaries” like a heating element. Electrolysis does not occur: the cathode and anode are continuously interchanged (frequency 50 Hz). Oscillations of ions occur with the release of energy that the coolant successfully absorbs.
An electric heating boiler, operating according to this principle, allows you to save up to 40% of electricity.
Dry running cannot disable equipment; scale deposits do not provoke the destruction of electrodes: only a reduction in boiler power is possible.
The dimensions of the ionization chamber are compact – the heat carrier heats up almost instantly; the pressure increases, reaching the required value without auxiliary mechanisms such as a circulation pump.
The electrode type of boilers has a high (up to 96%) efficiency, reliable and durable.
Disadvantages of equipment:
- the inability to connect to the network through an RCD;
- only special antifreezes designated by the manufacturer can act as a heat carrier;
Electric boilers on resistive and induction elements
Such boilers are some exotic. Resistive heating is somewhat reminiscent of electrode heating, but at the same time it has a number of advantages, in particular, it allows you to work with any coolants. There is no thermal barrier (heating layer – base), respectively, it becomes possible to optimize the capabilities of the model and at the same time reduce its power consumption.
In resistive boilers, the fuel element is evenly distributed over the surface of the heater – it does not come in contact with the coolant. It is made in the form of a metal pipe with an insulating layer, on which a spiral-like resistive layer (mainly tungsten) is applied. Electric current, heating the flow tank (pipe), heats and the coolant.

Installing an electric boiler is much easier than installing other heating equipment
Boilers that implement the principle of electromagnetic induction are also worthy of consumer attention. This installation has a design similar to a two-circuit transformer. The primary circuit is a magnetic system, and the secondary is a heat exchange device. In it, under the influence of an alternating field, currents are induced, causing heating, which is subsequently transferred to the coolant. The main advantages of induction boilers are electrical safety, work with almost all coolants.
Among the shortcomings – a rather high price, heavy weight, impressive dimensions.
How to calculate the required boiler power?
To do this, you can use the elementary ratio: for every 10 m? premises (with a ceiling height of about 3m) requires about 1 kW. Although, it is worth noting that this formula is approximate, because in addition to the height of the ceilings and the area, the determination of the required power is influenced by the mass of related factors: materials used in the construction of the house; how the building is insulated; number of windows, dimensions thereof; region of residence.
Purchase and operation: everything is relative
We will consider in stages all the costs that the purchase, installation and operation of an electric unit will cause you to compare and compare this type of heating equipment with other offers in the construction market.
Electric or gas?
The fact that gas is cheaper than electricity, as they say, is understandable for a hedgehog. If there is a gas main nearby the building (house), the choice becomes obvious. But remember that in addition to the cost of energy, there are many more aspects that must be considered:
- equipment cost – the “average” electric boiler is cheaper than a gas counterpart;
- installation cost – installation of electrical equipment will also be much cheaper;
- an electrical device is structurally simpler and does not need, unlike a gas, constant maintenance;
Electricity or liquid fuel?
The cost of electricians, of course, is slightly higher than the cost of liquid fuel. In the case of an electric boiler, you only need the boiler itself, while for the liquid fuel you will have to purchase additional “accessories”. As for installation, maintenance and design features, everything is similar to a gas device.

Turning on the electric boiler
Electricity or solid fuel?
Work in automatic mode, ease of maintaining the necessary temperature for comfort – the main advantages of electric boilers over solid fuel counterparts.
The combined use of an electric and solid fuel boiler is a fairly common “union”.
Electric boilers – reviews
Most people refuse electric boilers for obvious reasons. The first is space electricity bills. Secondly, network outages.
But at the same time, users note a lot of indisputable advantages of this equipment:
- low price;
- ease;
- compactness;
- ease of installation;
- space saving in the room;
- simplicity of operation;
- no need to mount a chimney;
- do not require special care, cleaning;
- are silent;
- do not create odors;
- no harmful emissions.
Having weighed all the pros and cons, you will surely be able to find a type of heating suitable for your native monastery that would completely satisfy all your needs, and most importantly – financial opportunities.






