How to ground in a private house
Electricity has long been perceived by us as a given. This benefit of civilization, familiar from childhood, opens up a ton of opportunities, and we willingly accept the benefits. Most of us do not care about the arrangement and principles of the power grid, we are quite satisfied with the role of a simple consumer. If a resident of a high-rise building can get away with such an understanding of the issue, then the owner of a private house must take into account all the features of the arrangement of electrical wiring and grounding in particular. Consider today how to ground in a private house.
Content
- Earthing switches, natural or artificial
- Work order
- Basic device rules
Grounding is necessary for protection. During the operation of some electrical appliances, an electric potential is generated on their conductive case, sometimes reaching 100 volts or more, it is impossible to exclude the possibility of this voltage or prevent its occurrence (each case is special, depending on the features of the device). If the house is connected to a three-phase power supply, and nearby electrical appliances are connected to different phases, then it is likely that the potential difference indicator will reach several hundred volts, which is a serious danger to life in case of contact with the case of such devices. Therefore, in accordance with modern standards of safe operation, all power electrical appliances in a private house (refrigerator, washing machine, electric stove, boiler, etc.) must be connected to a protective grounding system, then the potential will go through the grounding conductor to the ground.
The grounding device in a private house provides for the presence of a grounding conductor and a conductor laid from it to the input electrical panel. The earthing switch is a conductive part in electrical contact directly with the ground.
Earthing switches, natural or artificial
Natural grounding can be any metal structures that have contact with the ground, for example, metal pipes of underground water pipes, metal (except aluminum) shells of armored cables laid in the ground, reinforced concrete foundation structures.
It is forbidden to use gas pipelines, central heating and sewage pipes, as well as any pipelines with explosive and combustible substances as grounding conductors.
In accordance with the PUE standards, grounding of electrical installations up to 1 kV can be carried out using natural grounding conductors, if their resistance or contact voltage with the installation case does not exceed permissible values. The possibility of using such grounding conductors should be determined by appropriate calculations. In the absence or impossibility of using natural grounding conductors, the grounding device in a private house is carried out using artificial grounding conductors, which can be made independently. It is allowed to use steel, galvanized or copper grounding electrodes with a round, rectangular, angular, pipe section profile, the main thing is that they should not be painted or have any other insulation coating.
Grounding scheme of a private house
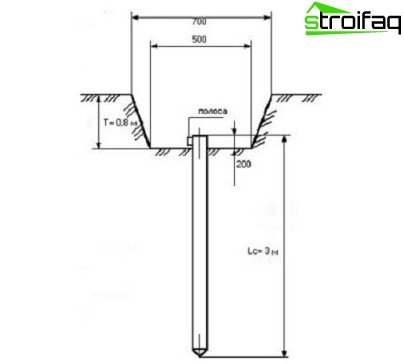
Earthing switches can be located in the ground vertically or horizontally at a depth below the level of freezing of the soil, the connection of grounding electrodes to each other is carried out only by welding, bolt connection is prohibited due to the possibility of oxidation. The choice of the optimal method of grounding device depends on the nature of the soil on the site, discussed below ground circuit A private home is the easiest and most reliable option. Before starting work, it is necessary to conduct measurements, calculate the electrical resistance of the soil, draw up a project of work, then based on the data obtained, calculate the length of the grounding electrodes and the amount of materials used.
Work order
At a distance of 5-10 m from the house, not far from the input switchboard, a trench should be dug, approximately half a meter deep (the depth of the trench may be greater, depending on the freezing parameters of the soil), repeating an equilateral triangle with grounding electrodes 1 in length 5–3 m (the length of the electrodes depends on the resistance of the soil), the electrodes can also be placed linearly, but in any case, the distance between them should be no less than their length. As the electrodes, you can use steel rods (the minimum diameter of a round rod is 16 mm), metal corners and profiles (the minimum permissible cross-sectional area of a rectangular and angular profile is 100 mm, with a wall thickness of 4 mm or more) and steel pipes (minimum diameter 32 mm with wall thickness from 3.5 mm).

To facilitate driving into the ground, the ends of the electrodes are sharpened
To facilitate driving in the electrodes, it is necessary to sharpen their ends; in hard soils, drilling will be required. After driving in the electrodes, they are interconnected by welding with a metal strip (cross-sectional area from 48 mm2, thickness from 4 mm). The same strip is used as a conductor leading from the ground electrode to the main ground bus of the input distribution board, the place of its entry into the building is indicated by the corresponding sign.

Grounding connection to the grounding bus of the input electrical panel
After leaving the ground, a conductor is fastened to the strip using a bolted connection, connecting it to the main grounding bus of the input electrical panel. A copper (cross-section of at least 10 mm2), aluminum (at least 16 mm2) or steel (at least 75 mm2) wire is used as such a conductor. The main grounding bus should be copper or steel (use of an aluminum bus is not allowed), may be located inside the switchboard or separately from it, in a place easily accessible for maintenance.
In case of placement inside the input device, the PE bus is used as it, when separately placed, the cross section of the ground bus should not be less than the cross section PE of the conductor of the supply line. It is also necessary to provide for disconnecting the conductors connected to the bus.

Connection of grounding electrodes with a metal strip
After completion of work, all trenches should be covered with homogeneous soil, preferably with a small amount of stones. It is necessary to measure the resistance of the grounding circuit, the indicator should not exceed 4 ohms. Grounding wiring in the house is laid together with chains of electrical outlets and power electrical appliances, the lighting network does not need grounding.
Basic device rules
- In the case where there is a high probability of corrosion, it is advisable to use grounding conductors with a large cross section or to use grounding conductors with galvanic coating.
- It is important to consider the increase in resistance of grounding materials due to corrosion..
- The arrangement of grounding conductors in places where the earth is dried out under the influence of heat pipelines is not allowed.
- The electrode placement depth should be below the ground freezing level.
- The distance between the electrodes must exceed their length.
- The diameter or cross-sectional area of the electrodes must comply with the requirements of the PUE.
- The connection of the electrodes with each other should be carried out only by welding.
- The resistance of the entire grounding system should be no more than 4 ohms.
Information on how to make grounding in a private house will undoubtedly tell only a general idea of a serious and responsible process. In any case, the work requires appropriate qualifications.