Undoubtedly, a well-made base provides longevity of the floor, its strength, wear-resistant and aesthetic characteristics. It can be a construction on logs, a floor with height adjustment, concrete or dry screed. In each case, the materials must comply with the functional parameters of a particular room. Therefore, the rough floor in a wooden house must be equipped, adhering to certain rules, which will be discussed.
Content
- What is called a rough floor
- Sub floor device
- Log floors
- Adjustable floor
- Screed – wet and dry
What is called a rough floor
The rough floor is a rather broad concept, which does not have an unambiguous definition. It is because of misinterpretation that confusion very often arises.
For example, a rough floor is the basis for laying laminate, linoleum, parquet. Basically, the flooring is arranged from sheets (OSB, chipboard, plywood), as well as from boards laid on logs. The main purpose of such a floor is to level the base plane and load distribution.

Sheet materials
This term is also called the lower layer of the double plank floor, used with a rare arrangement of floor beams and logs. At the same time, the boards of the subfloor are laid diagonally. Due to the multidirectionality of the fibers, such a combined coating gains additional strength.
But there is another concept of the rough floor – the lower layer of the insulated double overlap. Such a boardwalk performs the functions of retaining waterproofing and insulation.
Sub floor device
The floor is a kind of suitcase with a double bottom, since under the outer layer there is a base called the “rough floor”. The final result directly depends on the state of this basic coating: a tubercle, slight curvature or other defects will inevitably manifest themselves on the front side in the future. Therefore, just leveling is not enough, it is necessary to carry out the construction process so that the subfloor “stands still”, that is, does not crack, does not peel and does not break into pieces.
It should be noted that the creation of a strong, stable and even rough floor is not an easy task, but it can be done. True, until recently, this process was considered almost the longest and most laborious stage of repair. Fortunately, new technologies have radically changed the situation, because specialized building mixtures have simplified the construction of the subfloor. The leveling quality has reached a higher level, but cement-sand screed can not be discounted. Their main trump card is low cost (in most cases, sand is used for traditional leveling). If you delve into the essence of the issue and conduct a comparative analysis, you can understand that the benefit is small: the cement-sand floor has several disadvantages. And the leveling layer from the building mixture is one step ahead: does not need steel reinforcement, does not shrink, does not peel, does not crack, and also quickly sets and hardens.
Important: the current deviation rate is also observed (no more than 2 mm on 2 m of the surface), but subject to unconditional implementation of the instructions.
A rough floor is a collection of layers that provide an even and solid foundation for the finish coating. It consists of:
- screed – is done in the case when you need to align the base and hide the wires;
- waterproofing – preventing the penetration of water through the floor;
- the underlying layer – creating a uniform load;
- layer – a link with the underlying floor;
- heat and sound insulation.
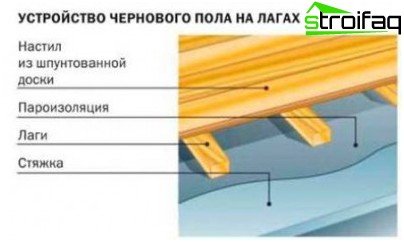
Log floors
Today it is, though not the most popular, but well-known technology. Logs – wooden or plastic bars, which are located strictly horizontally.

The floor on the logs is a traditional construction for wooden buildings, providing ventilation and the ability to lay in the underground communication space
Their main advantage is the absence of wet processes, and thanks to the air gap, the wooden flooring does not rot, is ventilated and can be rationally used for laying utilities.
Important: it is advisable to fill the distance between the bars with soundproofing materials..
The installation of the floor on the logs has its own nuances:
- the distance between adjacent lags is observed – 40 cm;
- correct and accurate leveling of the floor (zero slope);
- a gap to the wall (2-3 cm) – in the future it will be covered by a baseboard;
- on the logs the crate is attached, on top – a sheet of plywood or an OSB plate;
- the best option for laying – unscrewing, as if with brickwork;
- the edge of the plywood is strengthened with a gap of 2 mm, that is, both sheets should be on the log. This principle eliminates squeaking;
- if the plywood thickness is not enough, then another layer is laid;
- plywood at the ends and from the side of the lag is treated with an antiseptic.
Adjustable floor
This is a fairly new way of creating a rough coating and is very relevant in the case when it is necessary to raise the floor level by 2-12 cm. Its device is characterized by simple installation and simple construction. Such floors are used not only in private homes, in offices, too, besides under them you can reliably hide communications and mount sound and heat insulation. Most often, the adjustable floor is used where large differences in height occur, because in other ways it is difficult to level.

Adjustable floor – a modern ancestor of the floor on the logs, providing the ability to quickly build a rough floor
How to make a rough floor of this type? The idea is this: holes are drilled in plywood and plastic bushings (with internal thread) are inserted there. Metal dowels, nails, they are attached to concrete through the bolts of the rack. Plywood with bushings is put on the rack bolts, while the bolts can be rotated by lowering and lifting the sheets, that is, thus leveling the surface.
Screed – wet and dry
This option is the most common, the screed is wet (concrete) and dry. The latter is the backfill, which is a multi-layer structure. First, moisture and moisture insulation (utafol, plastic film, isospan) is placed on the surface, which is fixed with construction adhesive tape. Then a dry filling layer is distributed in a layer of 30-50 mm, it can be expanded clay, fine-grained slag, expanded perlite sand. Along the wall around the floor, a seam is made of elastic materials, they compensate for the thermal expansion of the base and exclude sound bridges.

After installing a dry screed, you can immediately proceed to the flooring
The top layer of such a screed is plywood panels, gypsum sheets, OSB, chipboard, ready-made modules with expanded polystyrene. The sheets are stacked in two layers and fastened with glue and self-tapping screws, but always with a displacement of the joints. The final stage – laying the finish coating.
Important: a prefabricated screed made of wood boards is coated with a flame retardant.
The advantages of a dry backfill are obvious: speed, the possibility of installation at any time of the year, convenience and good compensation for any unevenness of the floor.

Pouring concrete screed – a process that requires considerable labor and time, but relevant due to the cost-effectiveness
Classical concrete screed is a more traditional option, as the materials are inexpensive and public. It is not difficult to make such a rough floor with your own hands (on the ground):
- cleaning the base of debris;
- tamper;
- laying of the underlying layer – crushed stone (layer thickness 10 cm) and its further compaction;
- backfilling of sand (10 cm thick) and similar tamping;
- installation of heat and waterproofing – protection of the floor from dampness;
- applying cement-sand or gypsum mortar;
- rule alignment.
After carrying out these stages of work, the screed should dry. Drying can last a week or a month, it all depends on the thickness of the layer.
The classic screed makes it possible to equalize significant differences in height (up to 3 cm), forms a rigid surface, most suitable for finishing with linoleum, laminate, porcelain stoneware. But because of the rough texture, it is impossible to achieve a perfect, even layer, so an additional layer is used – the finish layer (self-leveling mixtures).
Bulk coating – a modern solution
Among the new technologies, one cannot but mention the bulk floor – a mixture of cement, polymeric materials (synthetic resins, polyurethane), reinforcing components that prevent the formation of microscopic cracks. In addition, the roughing and finishing screed in this case are one process, and this is a significant advantage.

Needle roller – leveling the surface of the bulk floor
The process of creating a bulk floor is to fill the base with a fluid mixture, which is leveled with a needle roller to remove air bubbles.
Compared to concrete screed, the polymer floor is thinner, so the drying time is reduced. As a rule, this indicator is indicated on the package and lasts a maximum of 2 weeks.
Intermediate layer – long-term guarantee
The structure of any floor, in particular covered with a laminate, carpet, parquet board, provides for the presence of a substrate: foamed polypropylene, extruded polystyrene foam, cork substrate, wood fiber boards. They can be attached to the subfloor in several ways:
- glue – it is the most popular, but with its application it is necessary to think over the installation in advance, since it is almost impossible to remove the glued underlying layer;
- double-sided tape – used for polyethylene materials;
- thermal tape and iron for welding – a fairly durable surface is created;
- self-tapping screws and building brackets – a quick method, but requiring skills: the brackets should not shoot very deep (so as not to deform the substrate) and not high (so as not to protrude the attachment points).
High-quality performance of the rough floor is the key to a trouble-free and long-term operation of the floor, an important structural element.






