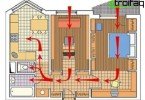
The need to build a system that provides normal air exchange in a closed room is dictated by the requirements of construction and sanitary-epidemiological standards. For normal life, for labor activity and just to maintain health, a person needs fresh air, it requires the removal of “exhausted” air mass, saturated with harmful gaseous substances, dust, bacteria and other contaminants. Properly completed ventilation design ensures perfect circulation of air flow, helps to form and stably maintain microclimatic conditions that are optimal for people in confined spaces.
Content
- Rules and regulations for ventilation
- Project Design Principles
- Phased design specifics
- Calculation of the balance of heat inflows of the feasibility study or the first stage
- Working draft – final product
Rules and regulations for ventilation
In rooms equipped poorly with ventilation duties, the content of carbon dioxide molecules and pathogens in the air rises sharply. The consequence is headaches, often recurring infectious diseases, drowsiness, excessive fatigue, in order to avoid what every person in the room needs:
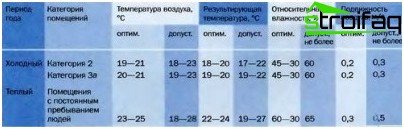
- minimum 20 m³ / hour (comfort maximum 60 m³ / hour) of fresh air coming from outside;
- relative humidity of air mass of 50%;
- air exchange rate 0.50 m / s.
The design of ventilation and air conditioning systems consists in the development of a route routing scheme and in the selection of equipment, the operation of which will provide microclimate standards regulated by SNiP 2.09.04-87
Professional design of ventilation and air conditioning systems, closely related to each other, is obliged to meet the above requirements, regulated by SNiPs. True, designers always try to ensure that the calculated air exchange slightly exceeds the regulatory minimums. And the exhaust air costs, equal by default to the intake, differ depending on the purpose of the room, for example:
- for the bathroom 50 m³ / h;
- minimum for a bathroom 25 m³ / h;
- for a kitchen room 90 m³ / h.
All household and utility “compartments”, including storage rooms, must also be provided with ventilation. All indicators of air flow are ultimately summarized, the result is a calculated hood. The air supply and exhaust in this volume should be provided by the designed system.
Project Design Principles
In fact, the design of ventilation systems consists in the selection of equipment and in the development of wiring methods that are reasonable according to technical, architectural, sanitary and economic criteria. The purpose of creating the project is to develop a system that can cope with the supply and removal of air in the calculated volume calculated for an apartment or a country house.
- The technical side of the issue is to meet the architectural and construction requirements. In the search and selection of the optimal technical means and wiring option, which ensures one hundred percent system operability, the ability to troubleshoot problems without problems and perform warranty service. The author of the project needs to choose equipment that not only performs its job perfectly, but also serves the maximum time. Basic equipment and additional equipment is selected taking into account the category to which the premises belong according to fire and explosive criteria.
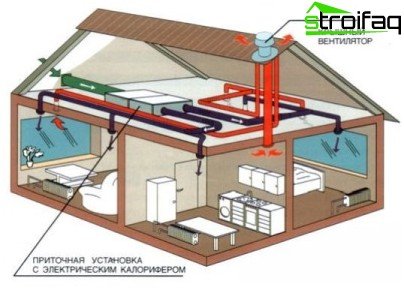
The ventilation project should not only guarantee trouble-free operation of the system, but also provide free access to all ventilation chambers and nodes
- Whenever possible, the design of ventilation and air conditioning should not violate the “image” of the building created by the architect. Changes made due to the installation of units and ducts should not catastrophically spoil the facades and interior paintings.

Examples of the location of outdoor units of climate systems: on the right, an unsuccessful solution, on the left, the optimal hidden option
- The removal of contaminated air and the supply of fresh clean air mass must meet sanitary and epidemiological requirements. The designer must find a solution so that the noise from the operation of the devices does not interfere with the owners and does not bother the neighbors.
- An important economic aspect and the choice of the cheapest scheme, on the basis of which the design and installation of ventilation systems will be carried out. The desire to save should not cause a loss of quality.
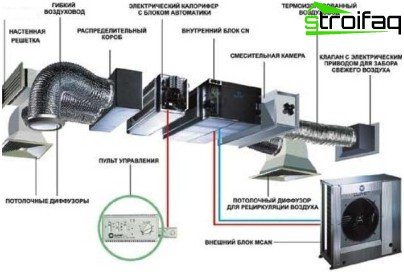
The project of supply and exhaust ventilation is to search and develop the best option that perfectly copes with the solution of technical, architectural, sanitary and economic issues
Usually, several fundamentally different options are developed for an object. All of them are discussed with the customer. The client compares and evaluates each of the schemes, selects the best.
Phased design specifics
The rationale for starting development is the terms of reference for the design of ventilation, which often complements the task of developing the design of an air conditioning system. In the statement of work, it takes into account the uneven distribution of temperatures at the facility and in each room, which is necessary to adjust the calculations of air exchange.
Calculation of the balance of heat influx
When calculating heat inflows, internal and external heat loads are taken into account.
- The category of external loads includes positive and negative temperature factors, the occurrence of which is influenced by atmospheric and natural phenomena. They depend on the time of day and on the season; climatological standards of the region are used to determine them. This category includes heat loss through building structures in the cold season, heat entering the room in sunny, hot weather, etc..
- Internal loads are only positive. This is the heat generated by the owners themselves, as well as by lighting, heating, and other household appliances.
Aerodynamic calculations justify the choice of ventilation equipment, help to accurately determine the location for the installation of ventilation equipment and for laying tracks.

Often, designers try to place ventilation chambers outside the living quarters, and hide the ductwork with a hinged ceiling
Feasibility study or first stage
The feasibility study is developed at increased values. In the first “enlarged” approximation, the type, number and power of ventilation units is determined. In this case, the preliminary cost of the system planned for installation is established. At this stage, it is possible to make adjustments to the design of the supply and exhaust ventilation and the climate system, if the customer is not satisfied with the scheme for some aspects.
Working draft – final product
It is a detailed processing of a pre-created feasibility study. At this stage, calculations of air exchange, heat emissions are carried out with high accuracy, devices are selected, the number of air diffusers according to specific parameters is calculated. Next, wiring plans and axonometric diagrams are drawn, hydraulic and aerodynamic calculations are performed.
After obtaining the consent of the customer, a set of working diagrams, drawings with an explanatory note is sent to the SES and the fire inspection, then with all the required permits is transferred to the contractor.
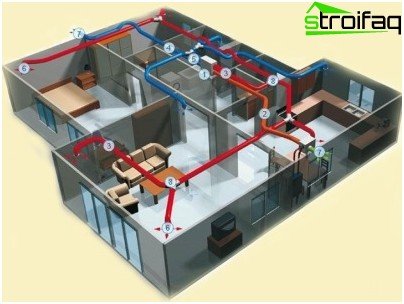
The scheme of supply and exhaust ventilation for the office: 1) Supply and exhaust installation, 2) Air duct for intake of external air, 3) Air duct of the supply system, 4) Air duct of the exhaust air, 5) Air duct of the exhaust system, 6) Diffusers, 7) External grilles, 8) Fittings
There is no doubt that the design of ventilation of a country house or the modernization of the climatic equipment of a city apartment should be carried out by specialists with appropriate education and experience in this field. However, the customer is not the last participant in the process, who has the right to make changes, demand alterations, track the path of creating the project and monitor the implementation of his ideas. He needs to be, as they say, “in the subject.” Information on the stages and specifics of development will help the property owner to insert a weighty word in time and stop violations.